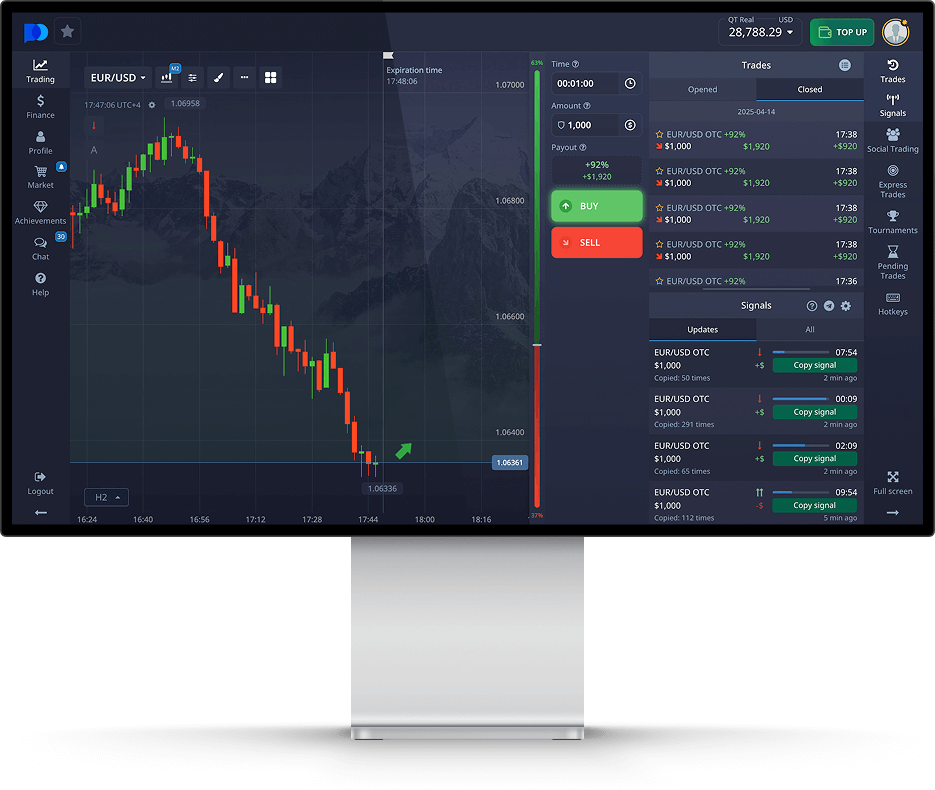
Understanding and Implementing the SMA Trading Strategy
The Simple Moving Average (SMA) is one of the most widely-used tools in technical analysis, allowing traders to smooth price data over a specific period for better decision-making. The SMA Trading Strategy торговая стратегия SMA is particularly favored for its simplicity and effectiveness, making it an essential part of a trader’s toolkit.
What is the SMA?
The Simple Moving Average (SMA) is calculated by adding a set of prices over a specific period and then dividing the total by the number of periods. For instance, the 10-day SMA considers the closing prices of the last 10 days. This averaging smooths out price fluctuations and provides traders a clearer indication of the overall trend.
How SMA Works
To understand how the SMA works, let’s break it down:
- Calculation: To calculate the SMA, you sum up the closing prices over a specific number of periods and divide by that number. For example, if you had the closing prices for a stock over the last 10 days as $20, $21, $22, $19, $20, $22, $23, $21, $20, and $24, the SMA would be: (20 + 21 + 22 + 19 + 20 + 22 + 23 + 21 + 20 + 24) / 10 = $21.
- Smoothing effect: SMA helps to eliminate the “noise” in the price data, allowing traders to identify trends more easily. A significant trend can usually be observed when the price is consistently above or below the SMA.

Types of SMAs
There are varying lengths of SMAs, each serving different purposes. Here are a few commonly used SMAs:
- Short-term SMA (e.g., 5- or 10-day): These are useful for identifying quick price movements and trends.
- Medium-term SMA (e.g., 20- or 50-day): These can indicate ongoing trends and are often used by swing traders.
- Long-term SMA (e.g., 100- or 200-day): These are used for identifying long-term trends and are valuable for position traders.
Benefits of the SMA Trading Strategy
The SMA Trading Strategy offers various benefits:
- Trend Identification: Perhaps the most significant advantage is its ability to help traders identify the overall market trend. Knowing whether a market is in an uptrend or downtrend can guide a trader’s decision-making.
- Support and Resistance Levels: SMAs can act as dynamic support and resistance levels, which can help traders set entry and exit points.
- Reduced Noise: By smoothing out price fluctuations, traders can focus on significant trends without the distraction of minor price movements.
How to Use the SMA in Your Trading Strategy
Implementing the SMA into a trading strategy involves several steps:
- Choosing the Period: Decide on the time frame that aligns with your trading style. Short-term traders might choose a 10-day SMA, while long-term traders might prefer a 200-day SMA.
- Setting Up Charts: Use trading platforms that allow you to overlay the SMA on price charts. This visual representation will help you see how the price interacts with the average.
- Identifying Trends: Look for crossovers where the price breaks above or below the SMA, indicating a potential trend change. For example, if price crosses above the 50-day SMA, it can signal a potential bullish trend, while crossing below it can indicate a bearish trend.
- Combining with Other Indicators: Many traders combine the SMA with other technical indicators such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or MACD for better accuracy. This multi-indicator approach can confirm trends and refine entry and exit points.
Strategies Incorporating SMA
Here are a couple of strategies that utilize SMAs effectively:
1. SMA Crossover Strategy
This strategy uses two SMAs – one short-term and one long-term. For instance, a 10-day SMA crossing above a 50-day SMA can indicate a buy signal, while the opposite crossover can indicate a sell signal. This method capitalizes on trend changes as they occur.
2. SMA Bounce Strategy
In this strategy, traders look for price bounces off the SMA line. If the price approaches the SMA and bounces back up, it can provide a buying opportunity, especially in an uptrend. Conversely, bounces below the SMA in a downtrend signal selling opportunities.
Risks and Limitations of the SMA Trading Strategy
While the SMA Trading Strategy has multiple advantages, it is essential to be aware of the risks and limitations:
- Lagging Indicator: SMAs are lagging indicators, meaning they react to price movements rather than predict them. This delay can result in missed trading opportunities.
- False Signals: Particularly in a choppy or sideways market, SMAs can generate false buy or sell signals, leading to potential losses.
- Over-reliance: Traders should not rely solely on SMAs; it’s crucial to incorporate other indicators and analysis techniques.
Conclusion
The SMA Trading Strategy is a powerful tool in any trader’s arsenal. Its ability to identify trends, reduce market noise, and set support and resistance levels makes it invaluable. However, like all trading strategies, it is most effective when used in conjunction with other indicators and methods. By understanding the principles of the SMA and practicing disciplined trading, traders can navigate the markets more effectively and enhance their trading success.
